Difference between revisions of "Hardware"
(→Video Capture Card) |
m (Shift section degrees down to start at 1, proper subsection structure) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* Check out [[LinuxMCE_Products|LinuxMCE Products]] for a list of products made for LinuxMCE | * Check out [[LinuxMCE_Products|LinuxMCE Products]] for a list of products made for LinuxMCE | ||
| − | + | =LinuxMCE hardware terms= | |
Here is a list of LinuxMCE-specific hardware terms. | Here is a list of LinuxMCE-specific hardware terms. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
*[[Orbiter]] - one or more lightweight portable devices used to control the system | *[[Orbiter]] - one or more lightweight portable devices used to control the system | ||
| − | + | =Minimum Requirements= | |
| − | + | ==CPU== | |
A LinuxMCE core-only machine can be run on a slower CPU such as a P3 if media encoding/decoding is not done on the core but, running the database, web server, and other system services can put resonable load on your CPU. | A LinuxMCE core-only machine can be run on a slower CPU such as a P3 if media encoding/decoding is not done on the core but, running the database, web server, and other system services can put resonable load on your CPU. | ||
| − | + | ==Motherboard== | |
Any Linux-compatible motherboard (95% chance your's will work) will run smoothly, give or take a few features (SPDIF, etc.) | Any Linux-compatible motherboard (95% chance your's will work) will run smoothly, give or take a few features (SPDIF, etc.) | ||
| − | + | ==RAM== | |
For a bare minimum core, 256MB+ of RAM is needed. For machines encoding/decoding media and/or running desktop applications 512MB+ is needed for smooth function. | For a bare minimum core, 256MB+ of RAM is needed. For machines encoding/decoding media and/or running desktop applications 512MB+ is needed for smooth function. | ||
| − | + | ==Hard Drive== | |
Your machines' hard drive(s) should be at least 4GB (to install the OS) plus as much as you want for media storage, network-boot images, etc. | Your machines' hard drive(s) should be at least 4GB (to install the OS) plus as much as you want for media storage, network-boot images, etc. | ||
| − | + | ==DVD/CD-ROM== | |
A DVD drive is required for installing with the Quick Install DVD. Without a DVD-ROM drive, the user is left to the CD install method, which requires a fresh install of Kubuntu 7.04, then a 2CD installation of LinuxMCE. | A DVD drive is required for installing with the Quick Install DVD. Without a DVD-ROM drive, the user is left to the CD install method, which requires a fresh install of Kubuntu 7.04, then a 2CD installation of LinuxMCE. | ||
| − | + | =Recommended Specifications= | |
| − | + | ==CPU== | |
Late model single-core or any dual or quad core processor is enough power to run a Core or Media Director. | Late model single-core or any dual or quad core processor is enough power to run a Core or Media Director. | ||
| − | + | ==Motherboard== | |
Any Linux-compatible motherboard. Can have built-in digital audio, Gb networking, HDMI, GPU, etc. | Any Linux-compatible motherboard. Can have built-in digital audio, Gb networking, HDMI, GPU, etc. | ||
| − | + | ==RAM== | |
1GB+ RAM should handle most setups. 4GB+ would require 64-bit OS which will be available in 0710. | 1GB+ RAM should handle most setups. 4GB+ would require 64-bit OS which will be available in 0710. | ||
| − | + | ==Hard Drive== | |
Most drives today offer more than enough storage space to run LinuxMCE, but you can add as much storage as you want via NAS, other machines, and other storage devices. | Most drives today offer more than enough storage space to run LinuxMCE, but you can add as much storage as you want via NAS, other machines, and other storage devices. | ||
| − | + | ==DVD/CD-ROM== | |
DVD-ROM drive is required for installing using the Quick Install DVD and a DVD+-RW drive is recommend for backing up media, burning CDs, etc. | DVD-ROM drive is required for installing using the Quick Install DVD and a DVD+-RW drive is recommend for backing up media, burning CDs, etc. | ||
| − | + | =User Feedback= | |
| − | + | ==CPU== | |
* A PIII/733MHz system can encode one video stream using the MPEG-4 codec using 480x480 capture resolution. This does not allow for live TV watching, but does allow for encoding video and then watching it later. | * A PIII/733MHz system can encode one video stream using the MPEG-4 codec using 480x480 capture resolution. This does not allow for live TV watching, but does allow for encoding video and then watching it later. | ||
* A developer states that his AMD1800+ system can almost encode two MPEG-4 video streams and watch one program simultaneously. | * A developer states that his AMD1800+ system can almost encode two MPEG-4 video streams and watch one program simultaneously. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
* A dual Celeron/450MHz is able to view a 480x480 MPEG-4/3300kbps file created on a different system with 30% CPU usage. | * A dual Celeron/450MHz is able to view a 480x480 MPEG-4/3300kbps file created on a different system with 30% CPU usage. | ||
* A P4 2.4GHz machine can encode two 3300Kbps 480x480 MPEG-4 files and simultaneously serve content to a remote frontend. | * A P4 2.4GHz machine can encode two 3300Kbps 480x480 MPEG-4 files and simultaneously serve content to a remote frontend. | ||
| − | + | ==FireWire== | |
You may use the [[Firewire]] output of the [[Motorola DCT6200]] or the [[Motorola SA3250|SA3250]]. | You may use the [[Firewire]] output of the [[Motorola DCT6200]] or the [[Motorola SA3250|SA3250]]. | ||
| − | + | ==Video Capture Card== | |
pcHDTV manufactures and supplies cards just for Linux and is now on its third generation of card, the HD-5500 available from http://www.pchdtv.com/ | pcHDTV manufactures and supplies cards just for Linux and is now on its third generation of card, the HD-5500 available from http://www.pchdtv.com/ | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
USB Capture Devices. | USB Capture Devices. | ||
| − | + | ==Sound Card== | |
The system needs a sound card or an on-board equivalent on the motherboard to play back and in most cases, to record sound. Any sound card that can be operated by the [[ALSA]] (Advanced Linux Sound Architecture) kernel modules will work with MythTV. However, some cards and drivers will provide better quality or compatibility than others. In particular, many audio devices included on motherboards can be problematic. | The system needs a sound card or an on-board equivalent on the motherboard to play back and in most cases, to record sound. Any sound card that can be operated by the [[ALSA]] (Advanced Linux Sound Architecture) kernel modules will work with MythTV. However, some cards and drivers will provide better quality or compatibility than others. In particular, many audio devices included on motherboards can be problematic. | ||
The usual practice for capturing the audio associated with the video is to run a cable from an audio output on the video capture card to the Line input on a sound card. However, some video capture cards provide on-board audio capabilities that work with the kernel btaudio module instead, thereby eliminating the need for a cable. This is useful if you will be using multiple capture cards in a single chassis, since each capture card will not need its own sound card. Note that a separate sound card is still required for playback when using btaudio, and that often the audio recorded in this way will be mono only. See the btaudio section for more information. | The usual practice for capturing the audio associated with the video is to run a cable from an audio output on the video capture card to the Line input on a sound card. However, some video capture cards provide on-board audio capabilities that work with the kernel btaudio module instead, thereby eliminating the need for a cable. This is useful if you will be using multiple capture cards in a single chassis, since each capture card will not need its own sound card. Note that a separate sound card is still required for playback when using btaudio, and that often the audio recorded in this way will be mono only. See the btaudio section for more information. | ||
| − | + | = See Also = | |
The [[:Category:Hardware|hardware category]] and it's sub categories. | The [[:Category:Hardware|hardware category]] and it's sub categories. | ||
| − | + | =External references= | |
* [[Useful Accessories]] | * [[Useful Accessories]] | ||
* [https://wiki.ubuntu.com/HardwareSupport Ubuntu hardware wiki] | * [https://wiki.ubuntu.com/HardwareSupport Ubuntu hardware wiki] | ||
Revision as of 17:23, 14 December 2007
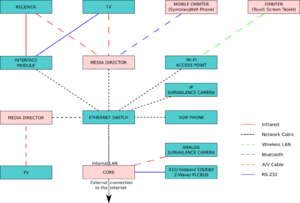
A basic LinuxMCE system can be set up with relatively modest PC and networking hardware. More advanced (though not necessarily expensive) systems can work with virtually any device that allows some form of input/output control capability. This might be through ethernet, infrared, RS232 or a home control protocol such as X10.
- Check out the hardware category for an organized list of hardware
- Check out LinuxMCE Products for a list of products made for LinuxMCE
Contents
LinuxMCE hardware terms
Here is a list of LinuxMCE-specific hardware terms.
- Core - a PC which is the center of your system
- Media director - PC devices which are connected to your core and provide
- Orbiter - one or more lightweight portable devices used to control the system
Minimum Requirements
CPU
A LinuxMCE core-only machine can be run on a slower CPU such as a P3 if media encoding/decoding is not done on the core but, running the database, web server, and other system services can put resonable load on your CPU.
Motherboard
Any Linux-compatible motherboard (95% chance your's will work) will run smoothly, give or take a few features (SPDIF, etc.)
RAM
For a bare minimum core, 256MB+ of RAM is needed. For machines encoding/decoding media and/or running desktop applications 512MB+ is needed for smooth function.
Hard Drive
Your machines' hard drive(s) should be at least 4GB (to install the OS) plus as much as you want for media storage, network-boot images, etc.
DVD/CD-ROM
A DVD drive is required for installing with the Quick Install DVD. Without a DVD-ROM drive, the user is left to the CD install method, which requires a fresh install of Kubuntu 7.04, then a 2CD installation of LinuxMCE.
Recommended Specifications
CPU
Late model single-core or any dual or quad core processor is enough power to run a Core or Media Director.
Motherboard
Any Linux-compatible motherboard. Can have built-in digital audio, Gb networking, HDMI, GPU, etc.
RAM
1GB+ RAM should handle most setups. 4GB+ would require 64-bit OS which will be available in 0710.
Hard Drive
Most drives today offer more than enough storage space to run LinuxMCE, but you can add as much storage as you want via NAS, other machines, and other storage devices.
DVD/CD-ROM
DVD-ROM drive is required for installing using the Quick Install DVD and a DVD+-RW drive is recommend for backing up media, burning CDs, etc.
User Feedback
CPU
- A PIII/733MHz system can encode one video stream using the MPEG-4 codec using 480x480 capture resolution. This does not allow for live TV watching, but does allow for encoding video and then watching it later.
- A developer states that his AMD1800+ system can almost encode two MPEG-4 video streams and watch one program simultaneously.
- A PIII/800MHz system with 512MB RAM can encode one video stream using the RTjpeg codec with 480x480 capture resolution and play it back simultaneously, thereby allowing live TV watching.
- A dual Celeron/450MHz is able to view a 480x480 MPEG-4/3300kbps file created on a different system with 30% CPU usage.
- A P4 2.4GHz machine can encode two 3300Kbps 480x480 MPEG-4 files and simultaneously serve content to a remote frontend.
FireWire
You may use the Firewire output of the Motorola DCT6200 or the SA3250.
Video Capture Card
pcHDTV manufactures and supplies cards just for Linux and is now on its third generation of card, the HD-5500 available from http://www.pchdtv.com/
The Plextor ConvertX PVR devices are supported through Linux drivers available from http://www.plextor.com/english/support/LinuxSDK.htm. MythTV uses the Plextor to capture hardware encoded MPEG-4, so the host CPU requirements are low.
Hauppauge WinTV-PVR-USB2 (driver available at http://www.isely.net/pvrusb2/) emulates a PVR-x50 card. IP Recorder (RTSP, RTS, UDP)
MPEG-2, MPEG-4 and H.264 internet TS stream recording is supported using the IPTV recorder in MythTV. This recorder expects the channels to be supplied as a m3u playlist. If your DSL/Fiber provider supplies television service, but does not provide a m3u playlist for the channels, you can construct one for your own use. You do not need to download it from the same server as the streams themselves, and can also read it from a file if this is more convenient.
If your provider uses 5C encryption on a particular channel, you won't be able to get any content. DBoxII or other devices running Neutrino
You may use the Ethernet port of an DBoxII or a similar device to capture MPEG2. Your set top box has to be running the Neutrino GUI. USB Capture Devices.
Sound Card
The system needs a sound card or an on-board equivalent on the motherboard to play back and in most cases, to record sound. Any sound card that can be operated by the ALSA (Advanced Linux Sound Architecture) kernel modules will work with MythTV. However, some cards and drivers will provide better quality or compatibility than others. In particular, many audio devices included on motherboards can be problematic.
The usual practice for capturing the audio associated with the video is to run a cable from an audio output on the video capture card to the Line input on a sound card. However, some video capture cards provide on-board audio capabilities that work with the kernel btaudio module instead, thereby eliminating the need for a cable. This is useful if you will be using multiple capture cards in a single chassis, since each capture card will not need its own sound card. Note that a separate sound card is still required for playback when using btaudio, and that often the audio recorded in this way will be mono only. See the btaudio section for more information.
See Also
The hardware category and it's sub categories.